攻击怪物
怪物的血条刷新逻辑,以及,怪物的血量属性同步逻辑都已经处理好了,接下来我们就可以编写逻辑,来让角色对怪物进行攻击。
1.给怪物添加受伤函数
在上一节,我们让怪物的血量进行了随机刷新,这么做是为了测试。现在我们需要将测试代码删除,然后向 MonsterScript 脚本中添加正确的受伤函数,受伤函数主要用来控制怪物的血量,以及控制怪物的死亡与复活。
MonsterScript脚本:
此次逻辑添加的要点:
① 添加了客户端调用,服务端生效的hurtOnServer函数,用来对血量属性进行变更。
② 当怪物血量降到0时,就关闭怪物模型的显示,达到怪物死亡的效果。
③ 添加了复活时间属性,用来设置怪物的复活时间。
④ 添加了只在客户端执行的hurt函数,用来在造成伤害前判断怪物是否死亡。
ts
import MonsterUI from "./UI/MonsterUI"
@Component
export default class MonsterScirpt extends Script {
@Property({ displayName: "怪物名" })
monsterName: string = ""
@Property({ displayName: "最大血量" })
maxHP: number = 100
@Property({ displayName: "复活时间(秒)" })
time: number = 2
@Property({ replicated: true, onChanged: "onHPChanged" })
nowHP: number = 100
private monsterUI: MonsterUI = null
/** 当脚本被实例后,会在第一帧更新前调用此函数 */
protected onStart(): void {
if (SystemUtil.isClient()) {
// 获取世界UI
let worldUI = this.gameObject.getChildByName("世界UI") as UIWidget
// 创建怪物UI
this.monsterUI = UIService.create(MonsterUI)
// 将怪物UI显示在世界UI上
worldUI.setTargetUIWidget(this.monsterUI.uiWidgetBase)
this.monsterUI.init(this.monsterName, this.maxHP)
}
if (SystemUtil.isServer()) {
this.nowHP = this.maxHP
setInterval(() => {
// 将血量更新的逻辑,写在服务端
this.nowHP = Math.floor(Math.random() * 100)
}, 1000)
}
}
private onHPChanged() {
// 调用血条刷新的逻辑
if (this.monsterUI) {
this.monsterUI.freshHP(this.nowHP)
}
}
public hurt(damage: number) {
if (this.nowHP <= 0) { return 0 }
this.hurtOnServer(damage)
return damage
}
@mw.RemoteFunction(mw.Server)
private hurtOnServer(damage: number) {
// 扣血
this.nowHP = this.nowHP - damage < 0 ? 0 : this.nowHP - damage
// 死亡逻辑
if (this.nowHP <= 0) {
this.gameObject.setVisibility(false)
// 怪物复活
setTimeout(() => {
this.gameObject.setVisibility(true)
this.nowHP = this.maxHP
}, (this.time + 1) * 1000);
}
}
}import MonsterUI from "./UI/MonsterUI"
@Component
export default class MonsterScirpt extends Script {
@Property({ displayName: "怪物名" })
monsterName: string = ""
@Property({ displayName: "最大血量" })
maxHP: number = 100
@Property({ displayName: "复活时间(秒)" })
time: number = 2
@Property({ replicated: true, onChanged: "onHPChanged" })
nowHP: number = 100
private monsterUI: MonsterUI = null
/** 当脚本被实例后,会在第一帧更新前调用此函数 */
protected onStart(): void {
if (SystemUtil.isClient()) {
// 获取世界UI
let worldUI = this.gameObject.getChildByName("世界UI") as UIWidget
// 创建怪物UI
this.monsterUI = UIService.create(MonsterUI)
// 将怪物UI显示在世界UI上
worldUI.setTargetUIWidget(this.monsterUI.uiWidgetBase)
this.monsterUI.init(this.monsterName, this.maxHP)
}
if (SystemUtil.isServer()) {
this.nowHP = this.maxHP
setInterval(() => {
// 将血量更新的逻辑,写在服务端
this.nowHP = Math.floor(Math.random() * 100)
}, 1000)
}
}
private onHPChanged() {
// 调用血条刷新的逻辑
if (this.monsterUI) {
this.monsterUI.freshHP(this.nowHP)
}
}
public hurt(damage: number) {
if (this.nowHP <= 0) { return 0 }
this.hurtOnServer(damage)
return damage
}
@mw.RemoteFunction(mw.Server)
private hurtOnServer(damage: number) {
// 扣血
this.nowHP = this.nowHP - damage < 0 ? 0 : this.nowHP - damage
// 死亡逻辑
if (this.nowHP <= 0) {
this.gameObject.setVisibility(false)
// 怪物复活
setTimeout(() => {
this.gameObject.setVisibility(true)
this.nowHP = this.maxHP
}, (this.time + 1) * 1000);
}
}
}2.创建玩家模块
在脚本中编写代码时,很容易出现客户端与服务端混杂在一起的情况,并且客户端和服务端通信,还需要我们编写大量的事件来进行处理。
为了解决这两个问题,我们可以使用编辑器提供的代码框架:“模块管理”,来提高代码编写的效率以及代码结构的清晰度。
一个“模块”分为“客户端模块”与“服务端模块”,这二者我们可以各用一个脚本来进行处理。
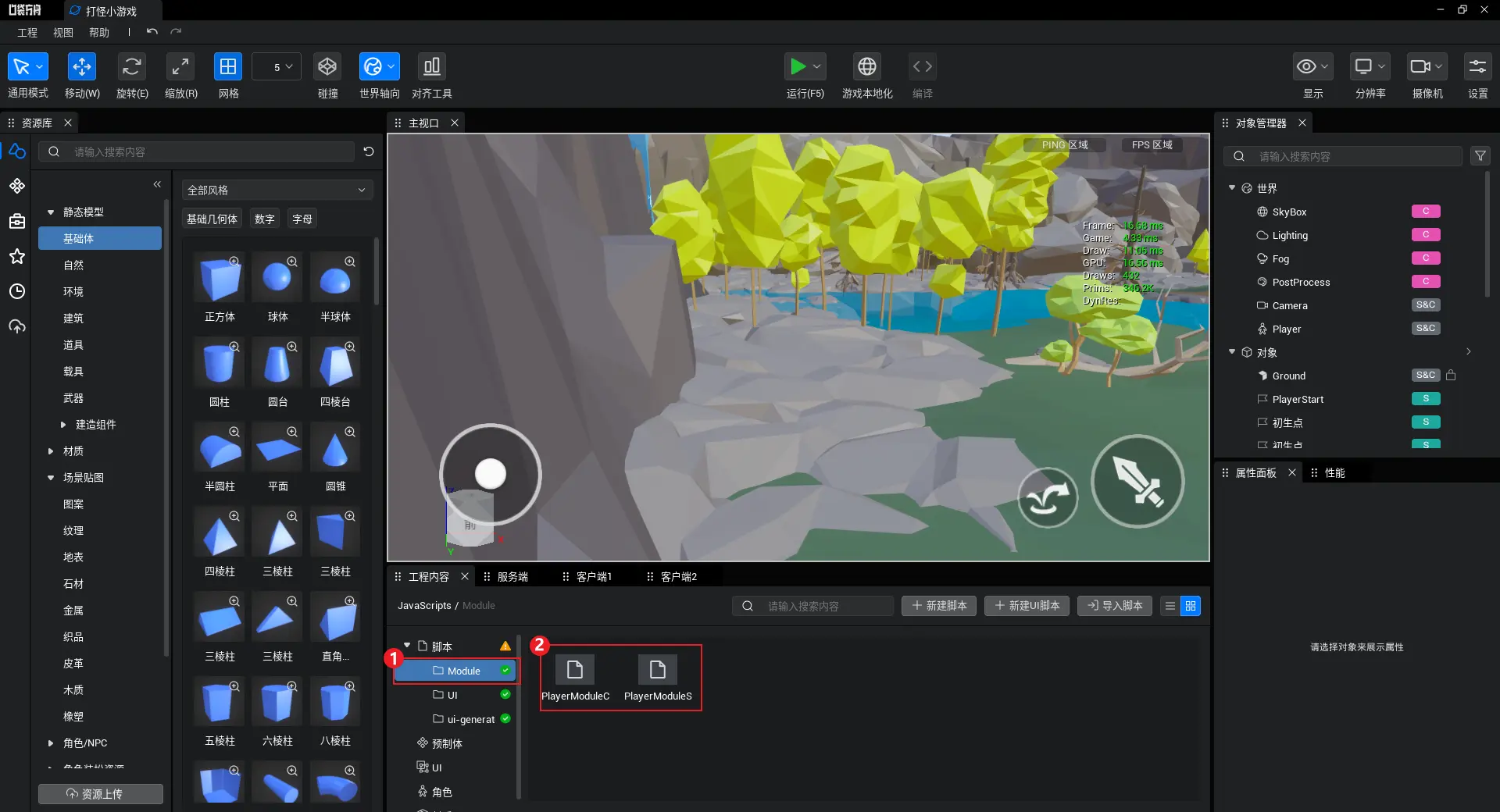
① 工程内容/脚本 中创建一个文件夹“Module”,用来专门存放模块管理相关的脚本
② 创建两个脚本,PlayerModuleC代表玩家客户端模块、PlayerModuleS代表玩家服务端模块
3.编写并注册模块脚本
新建好的两个脚本,其分别内容如下:
PlayerModuleC脚本:
ts
import { PlayerModuleS } from "./PlayerModuleS";
export class PlayerModuleC extends ModuleC<PlayerModuleS, null>{
protected async onStart(): Promise<void> {
console.log("角色客户端模块启动")
}
} import { PlayerModuleS } from "./PlayerModuleS";
export class PlayerModuleC extends ModuleC<PlayerModuleS, null>{
protected async onStart(): Promise<void> {
console.log("角色客户端模块启动")
}
} PlayerModuleS脚本:
ts
import { PlayerModuleData } from "./PlayerModuleData";
export class PlayerModuleS extends ModuleS<PlayerModuleC, null>{
protected onStart(): void {
console.log("角色服务端模块启动")
}
} import { PlayerModuleData } from "./PlayerModuleData";
export class PlayerModuleS extends ModuleS<PlayerModuleC, null>{
protected onStart(): void {
console.log("角色服务端模块启动")
}
} 模块脚本也具有生命周期函数,在上述两个脚本中我们都在onStart函数中添加了一行打印日志的逻辑。但现在运行游戏,代码并不会执行,我们需要将模块进行“注册”,注册后模块才能够正常运行。
创建GameStart脚本
① 新建脚本,命名为GameStart
② 将脚本挂载到一个双端物体上(这里挂载到了Ground对象上)
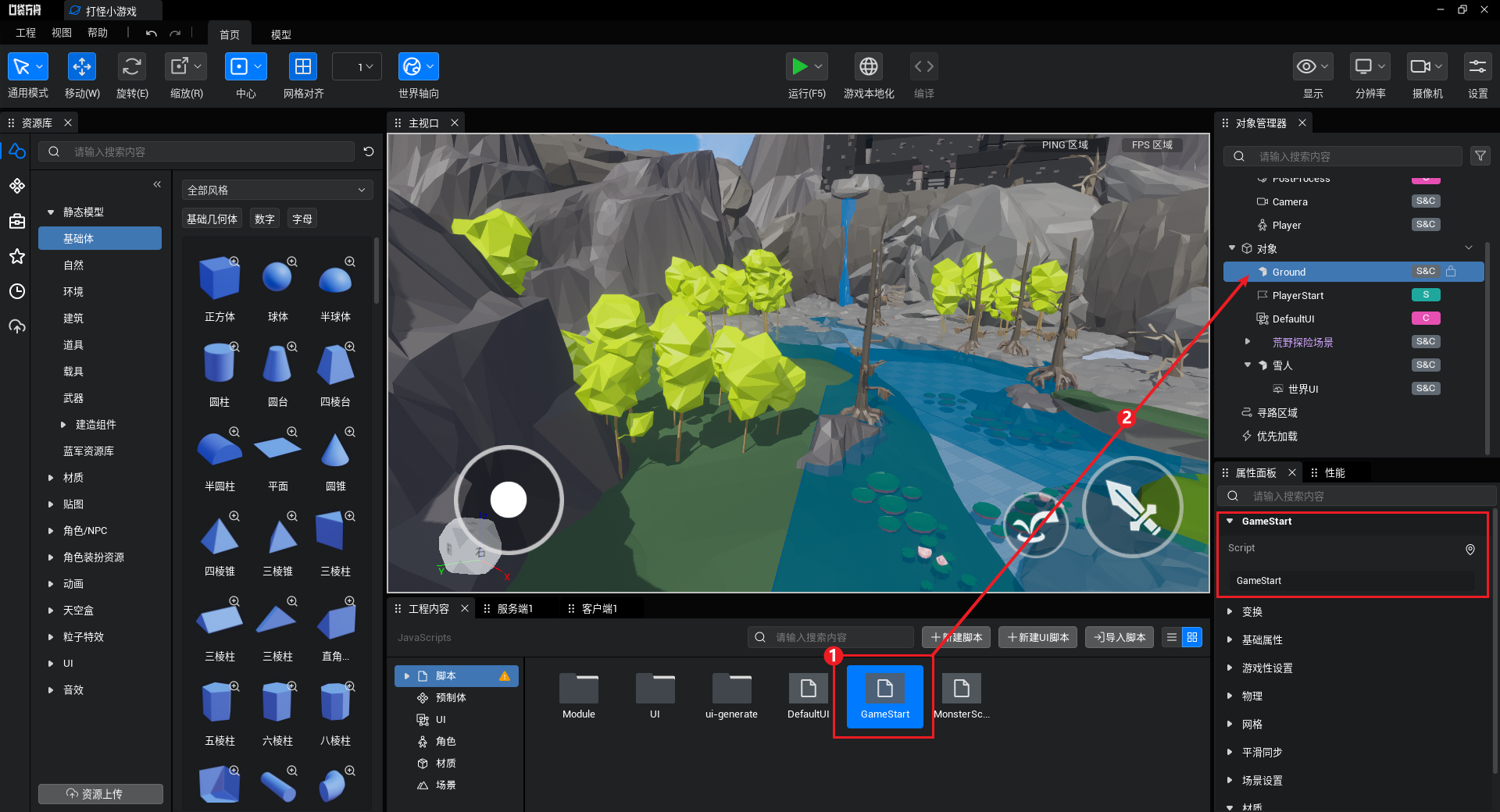
在GameStart脚本中添加注册模块的逻辑:
ts
import { PlayerModuleC } from "./Module/PlayerModuleC";
import { PlayerModuleS } from "./Module/PlayerModuleS";
@Component
export default class GameStart extends Script {
/** 当脚本被实例后,会在第一帧更新前调用此函数 */
protected onStart(): void {
ModuleService.registerModule(PlayerModuleS, PlayerModuleC, PlayerModuleData)
}
/**
* 周期函数 每帧执行
* 此函数执行需要将this.useUpdate赋值为true
* @param dt 当前帧与上一帧的延迟 / 秒
*/
protected onUpdate(dt: number): void {
}
/** 脚本被销毁时最后一帧执行完调用此函数 */
protected onDestroy(): void {
}
}import { PlayerModuleC } from "./Module/PlayerModuleC";
import { PlayerModuleS } from "./Module/PlayerModuleS";
@Component
export default class GameStart extends Script {
/** 当脚本被实例后,会在第一帧更新前调用此函数 */
protected onStart(): void {
ModuleService.registerModule(PlayerModuleS, PlayerModuleC, PlayerModuleData)
}
/**
* 周期函数 每帧执行
* 此函数执行需要将this.useUpdate赋值为true
* @param dt 当前帧与上一帧的延迟 / 秒
*/
protected onUpdate(dt: number): void {
}
/** 脚本被销毁时最后一帧执行完调用此函数 */
protected onDestroy(): void {
}
}4.范围检测
攻击怪物的前提是检测到怪物,在这里我们可以使用编辑器提供的范围检测API来进行检测。
在 PlayerModuleC 脚本中添加一个atk函数,用来进行范围检测:
① QueryUtil.sphereOverlap 是编辑器提供的球形范围检测接口
② QueryUtil.sphereOverlap 的第3个参数填true,即可以将检测范围绘制到游戏中
ts
import { PlayerModuleS } from "./PlayerModuleS";
export class PlayerModuleC extends ModuleC<PlayerModuleS, null>{
protected async onStart(): Promise<void> {
console.log("角色客户端模块启动")
}
public atk() {
// 范围检测
let result = QueryUtil.sphereOverlap(this.localPlayer.character.worldTransform.position, 100, true)
}
}import { PlayerModuleS } from "./PlayerModuleS";
export class PlayerModuleC extends ModuleC<PlayerModuleS, null>{
protected async onStart(): Promise<void> {
console.log("角色客户端模块启动")
}
public atk() {
// 范围检测
let result = QueryUtil.sphereOverlap(this.localPlayer.character.worldTransform.position, 100, true)
}
}我们可以让DefaultUI中的攻击按钮被按下时调用atk函数。
DefaultUI脚本:
使用ModuleService.getModule()获取模块
ts
import { PlayerModuleC } from "./Module/PlayerModuleC";
@UIBind('')
export default class DefaultUI extends UIScript {
private character: Character;
private anim1 = null;
/** 仅在游戏时间对非模板实例调用一次 */
protected onStart() {
// 省略代码
......
//点击攻击按钮,异步获取人物后执行攻击动作
attackBtn.onPressed.add(()=>{
Player.asyncGetLocalPlayer().then((player) => {
this.character = player.character;
AssetUtil.asyncDownloadAsset("61245").then((res : boolean) => {
if (res) {
if (!this.anim1) {
this.anim1= player.character.loadAnimation("61245");
this.anim1.slot = AnimSlot.Upper;
}
//角色执行攻击动作
if(this.anim1.isPlaying){
return
}else{
this.anim1.play();
ModuleService.getModule(PlayerModuleC).atk()
}
}
})
});
})
}
}import { PlayerModuleC } from "./Module/PlayerModuleC";
@UIBind('')
export default class DefaultUI extends UIScript {
private character: Character;
private anim1 = null;
/** 仅在游戏时间对非模板实例调用一次 */
protected onStart() {
// 省略代码
......
//点击攻击按钮,异步获取人物后执行攻击动作
attackBtn.onPressed.add(()=>{
Player.asyncGetLocalPlayer().then((player) => {
this.character = player.character;
AssetUtil.asyncDownloadAsset("61245").then((res : boolean) => {
if (res) {
if (!this.anim1) {
this.anim1= player.character.loadAnimation("61245");
this.anim1.slot = AnimSlot.Upper;
}
//角色执行攻击动作
if(this.anim1.isPlaying){
return
}else{
this.anim1.play();
ModuleService.getModule(PlayerModuleC).atk()
}
}
})
});
})
}
}进入游戏后,我们点击攻击按钮即可看到范围检测的效果

5.判断检测结果
范围检测能够将检测到的物体以数组的形式返回出来。此时我们的怪物模型在代码层面和其它模型是没有区别的,所以为了区分出怪物模型与其它模型,需要给怪物模型设置tag
在MonsterScript脚本中设置怪物模型的tag:
将怪物模型的tag设置为“Monster”
ts
import MonsterUI from "./UI/MonsterUI"
@Component
export default class MonsterScirpt extends Script {
@Property({ displayName: "怪物名" })
monsterName: string = ""
@Property({ displayName: "最大血量" })
maxHP: number = 100
@Property({ displayName: "复活时间(秒)" })
time: number = 2
@Property({ replicated: true, onChanged: "onHPChanged" })
nowHP: number = 100
private monsterUI: MonsterUI = null
/** 当脚本被实例后,会在第一帧更新前调用此函数 */
protected onStart(): void {
this.gameObject.tag = "Monster"
if (SystemUtil.isClient()) {
// 获取世界UI
let worldUI = this.gameObject.getChildByName("世界UI") as UIWidget
// 创建怪物UI
this.monsterUI = UIService.create(MonsterUI)
// 将怪物UI显示在世界UI上
worldUI.setTargetUIWidget(this.monsterUI.uiWidgetBase)
this.monsterUI.init(this.monsterName, this.maxHP)
}
if (SystemUtil.isServer()) {
this.nowHP = this.maxHP
setInterval(() => {
// 将血量更新的逻辑,写在服务端
this.nowHP = Math.floor(Math.random() * 100)
}, 1000)
}
}
private onHPChanged() {
// 调用血条刷新的逻辑
if (this.monsterUI) {
this.monsterUI.freshHP(this.nowHP)
}
}
public hurt(damage: number) {
if (this.nowHP <= 0) { return 0 }
this.hurtOnServer(damage)
return damage
}
@mw.RemoteFunction(mw.Server)
private hurtOnServer(damage: number) {
// 扣血
this.nowHP = this.nowHP - damage < 0 ? 0 : this.nowHP - damage
// 死亡逻辑
if (this.nowHP <= 0) {
this.gameObject.setVisibility(false)
// 怪物复活
setTimeout(() => {
this.gameObject.setVisibility(true)
this.nowHP = this.maxHP
}, (this.time + 1) * 1000);
}
}
}import MonsterUI from "./UI/MonsterUI"
@Component
export default class MonsterScirpt extends Script {
@Property({ displayName: "怪物名" })
monsterName: string = ""
@Property({ displayName: "最大血量" })
maxHP: number = 100
@Property({ displayName: "复活时间(秒)" })
time: number = 2
@Property({ replicated: true, onChanged: "onHPChanged" })
nowHP: number = 100
private monsterUI: MonsterUI = null
/** 当脚本被实例后,会在第一帧更新前调用此函数 */
protected onStart(): void {
this.gameObject.tag = "Monster"
if (SystemUtil.isClient()) {
// 获取世界UI
let worldUI = this.gameObject.getChildByName("世界UI") as UIWidget
// 创建怪物UI
this.monsterUI = UIService.create(MonsterUI)
// 将怪物UI显示在世界UI上
worldUI.setTargetUIWidget(this.monsterUI.uiWidgetBase)
this.monsterUI.init(this.monsterName, this.maxHP)
}
if (SystemUtil.isServer()) {
this.nowHP = this.maxHP
setInterval(() => {
// 将血量更新的逻辑,写在服务端
this.nowHP = Math.floor(Math.random() * 100)
}, 1000)
}
}
private onHPChanged() {
// 调用血条刷新的逻辑
if (this.monsterUI) {
this.monsterUI.freshHP(this.nowHP)
}
}
public hurt(damage: number) {
if (this.nowHP <= 0) { return 0 }
this.hurtOnServer(damage)
return damage
}
@mw.RemoteFunction(mw.Server)
private hurtOnServer(damage: number) {
// 扣血
this.nowHP = this.nowHP - damage < 0 ? 0 : this.nowHP - damage
// 死亡逻辑
if (this.nowHP <= 0) {
this.gameObject.setVisibility(false)
// 怪物复活
setTimeout(() => {
this.gameObject.setVisibility(true)
this.nowHP = this.maxHP
}, (this.time + 1) * 1000);
}
}
}设置完tag之后,我们便可以完善攻击函数了,让攻击函数能正确检测到怪物并对怪物造成伤害。
PlayerModuleC脚本:
此次添加逻辑的要点:
① 遍历范围检测的结果,排除是Character类型的情况,只判断模型tag为“Monster”的情况
② 使用getScripts从模型上获取到模型所挂载的所有脚本
③ 遍历获取到的脚本,找到MonsterScript脚本,并调用受伤函数
④ 添加了一个属性,作为角色的当前攻击力
ts
import MonsterScirpt from "../MonsterScirpt";
import { PlayerModuleS } from "./PlayerModuleS";
export class PlayerModuleC extends ModuleC<PlayerModuleS, PlayerModuleData>{
private _nowAtk: number = 50
protected async onStart(): Promise<void> {
console.log("角色客户端模块启动")
}
public atk() {
// 范围检测
let result = QueryUtil.sphereOverlap(this.localPlayer.character.worldTransform.position, 100, false)
// 筛选出怪物
for (let obj of result) {
if (obj instanceof Character) {
continue
}
if (obj.tag == "Monster") {
// 让怪物受伤
let scripts = obj.getScripts()
for (let script of scripts) {
if (script instanceof MonsterScirpt) {
let damage = script.hurt(this._nowAtk)
}
}
}
}
}
}import MonsterScirpt from "../MonsterScirpt";
import { PlayerModuleS } from "./PlayerModuleS";
export class PlayerModuleC extends ModuleC<PlayerModuleS, PlayerModuleData>{
private _nowAtk: number = 50
protected async onStart(): Promise<void> {
console.log("角色客户端模块启动")
}
public atk() {
// 范围检测
let result = QueryUtil.sphereOverlap(this.localPlayer.character.worldTransform.position, 100, false)
// 筛选出怪物
for (let obj of result) {
if (obj instanceof Character) {
continue
}
if (obj.tag == "Monster") {
// 让怪物受伤
let scripts = obj.getScripts()
for (let script of scripts) {
if (script instanceof MonsterScirpt) {
let damage = script.hurt(this._nowAtk)
}
}
}
}
}
}